Web technologies are far more intricate and complex than most people think. Behind the simple act of typing a URL into a browser and seeing a website load, many layers work harmoniously to deliver that content. Two such layers often used are the proxy server and the reverse proxy server. But what are these, and what’s the difference between them? Let’s delve into this.
What is a Proxy Server?
To understand the concept of a proxy server, imagine a middleman communicating on your behalf. A proxy server is an intermediary between a client (e.g., your computer) and the internet.
Instead of your computer communicating directly with a website, it first connects to a proxy server. The proxy server then retrieves the data from the website and sends it back to your computer. This process is beneficial for several reasons:
- Privacy: The website you’re communicating with only sees the proxy server’s IP address, not yours. This adds an extra layer of privacy and anonymity to your online activities.
- Security: Proxy servers can provide security features like firewalls and web filters. They can block access to harmful websites before your computer connects.
- Speed and bandwidth: By caching (storing) web pages, proxy servers can speed up the loading of web pages that have been previously visited. This process reduces bandwidth and improves overall internet speed.
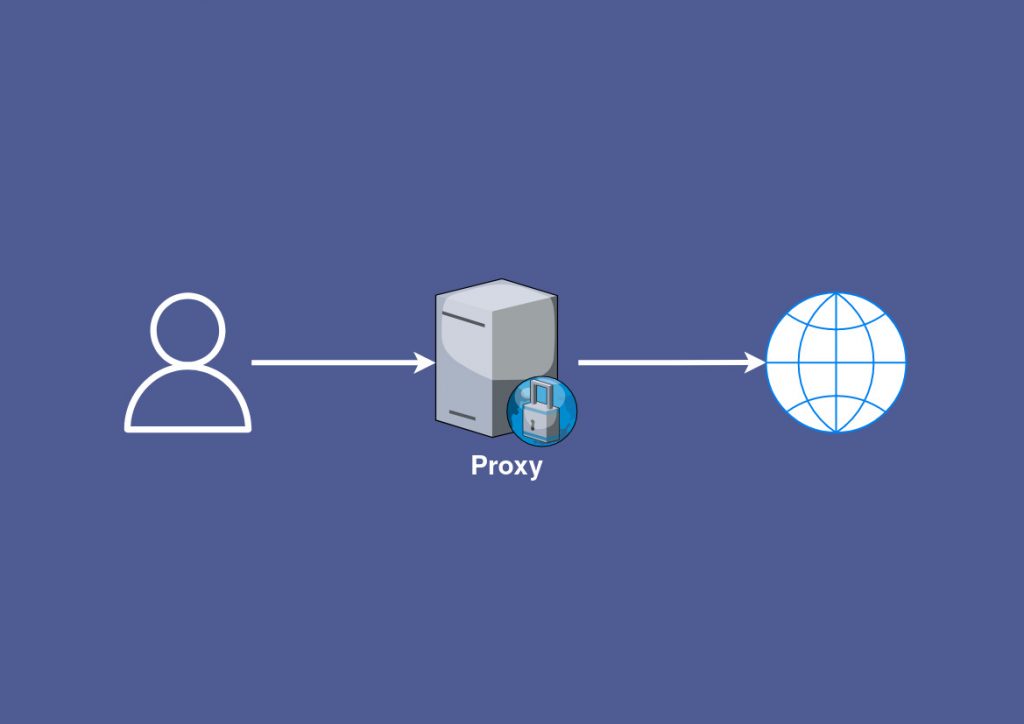
Proxy Server Example:
Let’s consider a real-world example. John works at a company that takes internet security very seriously. The company uses a proxy server to manage internet connections from their network to the outside world. Here’s how it works:
- John types the URL
www.example.cominto his web browser. - Instead of going straight to
example.com, the request goes to the company’s proxy server first. - The proxy server connects to
www.example.comon behalf of John’s computer. www.example.comsees the IP address of the proxy server, not John’s computer.- The proxy server retrieves the webpage from
www.example.comand forwards the content back to John’s computer.
In this scenario, the proxy server offers John’s company enhanced control, security, and privacy.
Proxy Server Technologies:
- Squid: Squid is an open-source proxy caching server. It caches frequently used content to increase the speed of response times while reducing bandwidth usage. Squid is widely used for its speed and ability to handle a large number of simultaneous connections.
- Privoxy: Privoxy is a non-caching web proxy that focuses on privacy enhancement, filtering web content, and removing ads. It’s often used in conjunction with the Tor network to enhance user privacy.
- Microsoft Forefront Threat Management Gateway (TMG): While it’s no longer actively developed by Microsoft, TMG (formerly known as Internet Security and Acceleration Server) is a comprehensive gateway solution offering various features, including web proxy and firewall capabilities.
What is a Reverse Proxy?
A reverse proxy, as the name suggests, performs the opposite function of a proxy server. It acts as an intermediary for requests from clients seeking resources from servers. In other words, it takes requests from the internet and forwards them to servers within an internal network.
Here are the key benefits of using a reverse proxy:
- Load Balancing: A reverse proxy can distribute client requests across several servers, reducing the load on any one server and ensuring none get overwhelmed. This process increases the overall performance and speed of a website.
- Security and Anonymity: Just as a proxy server hides the client’s identity, a reverse proxy hides the identity of the web server. This feature provides an extra security layer, protecting the server from potential attacks.
- SSL Encryption: The reverse proxy can encrypt and decrypt data on behalf of the server, offloading the computational burden of SSL encryption from the server and enhancing its performance.
Reverse Proxy Example:
Now, let’s illustrate a reverse proxy using Netflix as an example. As a global streaming service, Netflix has millions of users attempting to connect and stream content simultaneously. Here’s how a reverse proxy comes into play:
- John wants to watch a movie on Netflix, so he navigates to the Netflix website and clicks on his chosen movie.
- His request is received by a reverse proxy server at Netflix’s data center.
- The reverse proxy server doesn’t provide the movie data itself. Instead, it forwards John’s request to one of many video streaming servers in Netflix’s internal network.
- Depending on current server loads, the reverse proxy chooses the most appropriate server to handle John’s request.
- The chosen server sends the movie data back to the reverse proxy, which then sends the data to John’s computer.
In this case, the reverse proxy server helps Netflix distribute load efficiently, ensures smooth streaming for all its users, and provides additional layers of security and anonymity for its servers.
Reverse Proxy Technologies:
- Nginx: Nginx is a popular open-source web server that also functions as a reverse proxy, load balancer, and HTTP cache. It’s known for its high performance, stability, and rich feature set.
- Apache HTTP Server with mod_proxy: While traditionally used as a web server, Apache can also work as a reverse proxy server when equipped with the
mod_proxymodule. This module provides basic proxy capabilities and extends to include load balancing functionality. - HAProxy: HAProxy stands for “High Availability Proxy”. It is an open-source software that provides a high-performance and highly-robust load balancer and reverse proxy. It is often used to improve the performance of websites by distributing their client requests across multiple servers.
- Microsoft Azure Application Gateway: Azure Application Gateway is a managed service from Microsoft Azure that provides a reverse proxy with security and performance features such as SSL offload, load balancing, and web application firewall capabilities.
By using these technologies, developers and system administrators can implement proxy or reverse proxy functionality depending on the needs of their applications or systems.
The Difference Between Proxy and Reverse Proxy
The fundamental difference between a proxy and a reverse proxy is the direction of the connection and the perspective:
- A proxy server is on the client’s side: It receives requests from the client, sends them to the internet, and returns the response to the client. It is mainly used for anonymity, privacy, security, and controlling internet usage.
- A reverse proxy server is on the server’s side: It receives requests from the internet, sends them to the appropriate server within an internal network, and returns the server’s response to the client. It’s mainly used for load balancing, enhancing security, and improving website performance.
While both technologies function as intermediaries, the distinction lies in who they serve. A proxy server serves the client, masking its activities on the internet. On the other hand, a reverse proxy serves the server, shielding it and distributing client requests to improve its performance and security.
In conclusion, understanding proxy and reverse proxy servers and their differences is essential in today’s internet-driven world. This knowledge can empower users to make informed decisions about their online security and privacy and improve their overall browsing experience.